Female Infertility
Infertility is defined as trying to get pregnant with frequent, unprotected sex for at least a year with no success.
Infertility results from female factors about one-third of the time and both female and male factors about one-third of the time. The cause is either unknown or a combination of male and female factors in the remaining cases.
Female infertility causes can be difficult to diagnose. There are many treatments, depending on the infertility cause. Many infertile couples will go on to conceive a child without treatment.

Male Infertility
Nearly 1 in 7 couples is infertile, which means they haven't been able to conceive a child even though they've had frequent, unprotected sexual intercourse for a year or longer. In up to half of these couples, male infertility plays at least a partial role.
Male infertility can be caused by low sperm production, abnormal sperm function or blockages that prevent the delivery of sperm. Illnesses, injuries, chronic health problems, lifestyle choices and other factors may contribute to male infertility.
The inability to conceive a child can be stressful and frustrating, but a number of treatments are available for male infertility.

High Risk Pregnancy
A high-risk pregnancy is one that threatens the health or life of the mother or her fetus. It often requires specialized care from specially trained providers.
Some pregnancies become high risk as they progress, while some women are at increased risk for complications even before they get pregnant for a variety of reasons.
Early and regular prenatal care helps many women have healthy pregnancies and deliveries without complications.

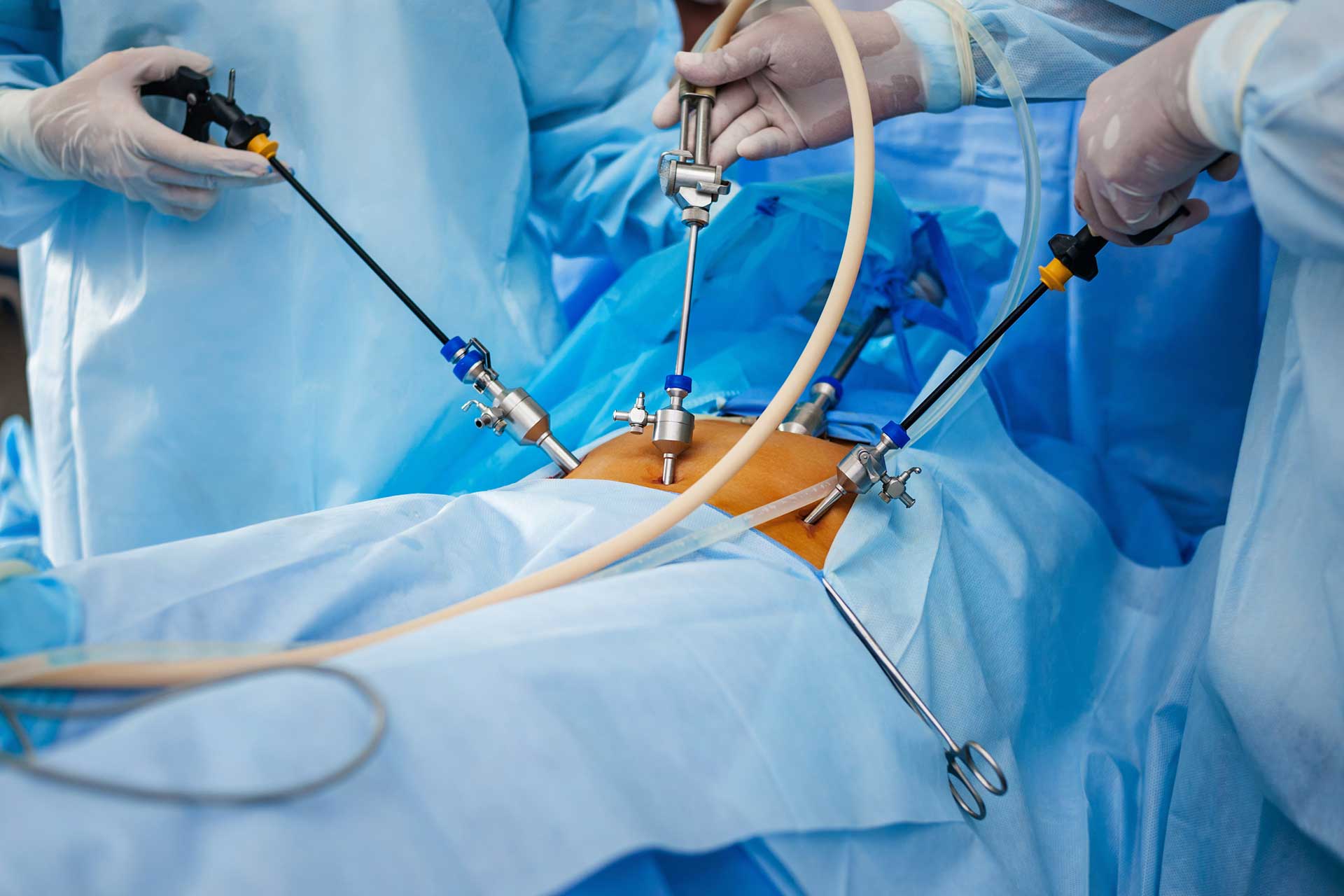
Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery
A laparoscope looks like a hysteroscope, but it is inserted into the pelvic and abdominal cavities to diagnose and treat gynecologic disorders. Instead of using fluid to expand the cavity, carbon dioxide gas is introduced to provide visualization of the internal organs. A camera is attached to guide the surgeon and to document the findings with photographs.
Laparoscopy has many uses, including the diagnosis and treatment of chronic pelvic pain, endometriosis, fibroid tumors, infertility, and ovarian cysts.
Many surgical procedures that used to be performed through larger abdominal incisions are now performed laparoscopically.
Vaginal Surgery
Vaginal reconstruction or vaginal rejuvenation surgery are the terms used for a wide range of procedures whose objectives are to repair or reconstruct the vagina. Vaginal surgery of this kind aims to reduce pain and improve the appearance, size, function and possibly the sensitivity of the vagina.
Reduction of pain is not the only positive result of vaginal surgery, many women discover a renewed self-confidence post-procedure.
Hysterectomy
An abdominal hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that removes your uterus through an incision in your lower abdomen. Your uterus — or womb — is where a baby grows if you're pregnant. A partial hysterectomy removes just the uterus, leaving the cervix intact. A total hysterectomy removes the uterus and the cervix.
Sometimes a hysterectomy includes removal of one or both ovaries and fallopian tubes, a procedure called a total hysterectomy with salpingo-oophorectomy (sal-ping-go-o-of-uh-REK-tuh-me).
A hysterectomy can also be performed through an incision in the vagina (vaginal hysterectomy) or by a laparoscopic or robotic surgical approach — which uses long, thin instruments passed through small abdominal incisions.
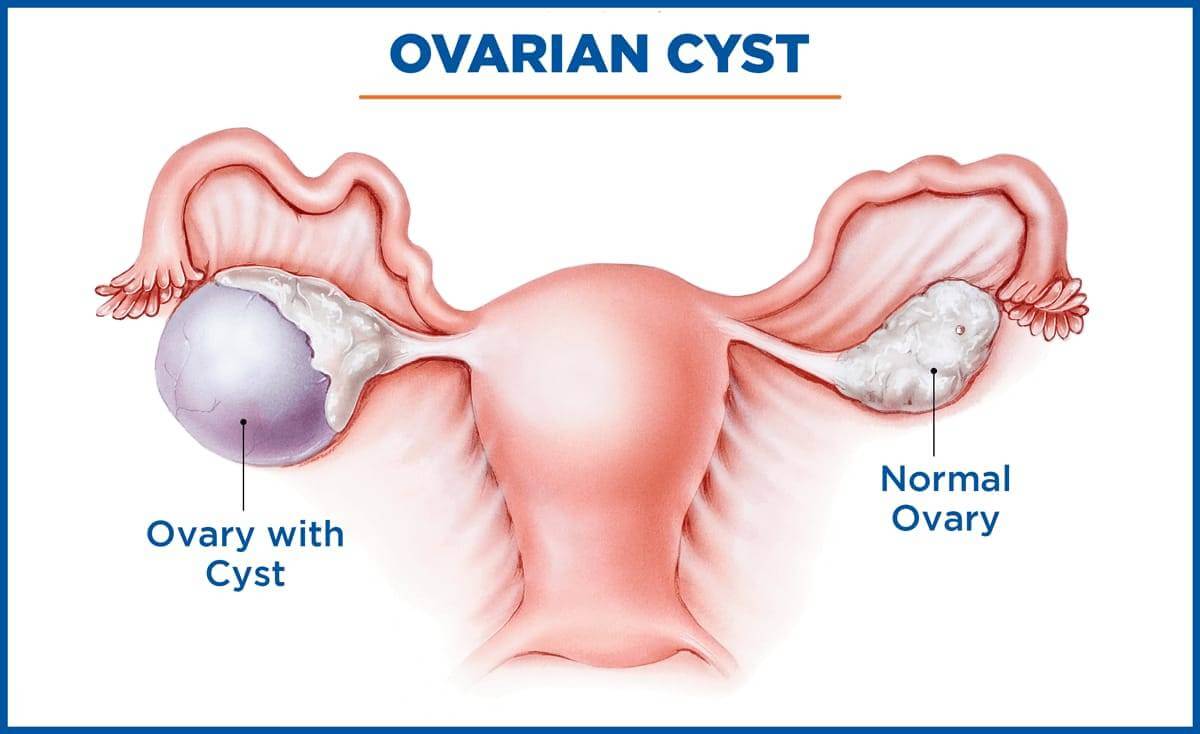
Ovarian Cystectomy
An ovarian cystectomy is surgery to remove a cyst from your ovary. Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgery technique that only uses a few small incisions in your lower abdomen.
Many women will have an ovarian cyst at some point during their lives. Commonly, cysts will cause little to no symptoms. However, if a cyst is causing painful or discomforting systems, surgical removal of the cysts may be the best treatment option. Some symptoms of an ovarian cyst include pelvic pain, especially during your period or sexual intercourse.
Before surgery begins, you will be given anesthesia to sleep. A laparoscope – a thin tube with a camera on the end – is inserted into the abdomen, usually at the sight of your navel, through a small incision. Additional incisions will be made on your abdomen. Air will be used in the abdomen to create more space between your abdominal wall and internal organs. Surgical instruments will be used to remove the cyst.
Menopausal Problems
Menopause is the time that marks the end of your menstrual cycles. It's diagnosed after you've gone 12 months without a menstrual period. Menopause can happen in your 40s or 50s, but the average age is 51 in the United States.
Menopause is a natural biological process. But the physical symptoms, such as hot flashes, and emotional symptoms of menopause may disrupt your sleep, lower your energy or affect emotional health. There are many effective treatments available, from lifestyle adjustments to hormone therapy.

Ovarian Tumor
Ovarian tumors are abnormal growths on the ovaries, the female reproductive organs that produce eggs. Ovarian tumors can be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant).
Many things can make you more likely to develop an ovarian tumor. Our team at Dignity Health will walk you through your initial exam, diagnosis, and any necessary treatments.
